Table of Contents
Case 17. Bypass Types and External Optical Bypass Management
The Bypass function enables transparent traffic pass-through without processing. The system includes the following levels of Bypass:
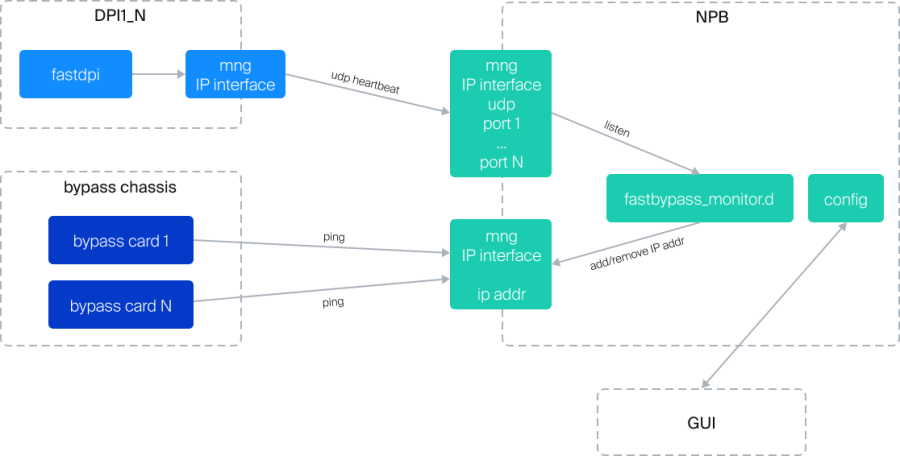
1. External Optical Bypass consists of a chassis and Bypass cards. Each card serves 1 or 2 links and independently monitors the signal level toward the NPB for specific links. If the signal falls below a certain level, an immediate switch to Bypass mode occurs. The card also performs an IP address availability check (ping Heartbeat) on the NPB. If the ping is lost, the cards switch to Bypass mode. The fastBypass process on the NPB ensures an external Optical Bypass switch in case of NPB failure or more than N DPI devices failing.
2. Software Bypass on the NPB enables traffic pass-through without forwarding to DPI devices. It is used for transparent pass-through of service traffic (BGP, MPLS). The following protocols possible to configure for transparent pass-through on the NPB:
- ARP
- LACP
- BFD
- MPLS
- LDP
- BGP
- IS-IS
- NDP
- Any Subnets
3. Software Bypass on the DPI enables traffic pass-through through DPI devices and is used for transparent pass-through of certain ASN traffic.
External Bypass Management
Each Bypass card has independent management. Bypass is managed with the fbypass_ctl utility. This utility includes a command set for enabling/disabling Bypass, launching the fastbypass_monitor service, and obtaining status.
The fbypass_ctl utility is an alias for a bash script. It can only be used in sudo mode. Before using the utility, enter sudo su - and the password.
After the utility, specify the following for Bypass management:
- Parameter
bp_module - Module number or
allto manage all Bypasses - Module number or
allto manage all cards - The command to execute
Examples of utility usage are provided in the corresponding section.
Available Commands
enable_bypass — set card to bypass mode (mode: manual, channel: bypass)
disable_bypass — set card to normal mode (mode: auto, channel: primary)
set_bypass_channel — set channel to bypass mode
set_primary_channel — set channel to primary mode
set_manual_mode — set card to manual mode
set_auto_mode — set card to auto mode
get_mode_state — return the card mode status
get_channel_state — return the card channel status
Utility Usage Examples
- Enable bypass on all modules and cards
fbypass_ctl bp_module all all enable_bypass
- Disable bypass on all modules and cards
fbypass_ctl bp_module all all disable_bypass
- Get mode status on all modules and cards
fbypass_ctl bp_module all all get_mode_state
- Get channel status on all modules and cards
fbypass_ctl bp_module all all get_channel_state
- Enable bypass on module zero and cards 1 and 3
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 1,3 enable_bypass
- Disable bypass on module zero and cards 7, 15, and 21
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 7,15,21 enable_bypass
- Get mode status on module zero and cards 7, 15, and 21
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 7,15,21 all get_mode_state
- Get channel status on module zero and cards 7, 15, and 21
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 7,15,21 all get_channel_state
- Set active channels on all sites to bypass mode (mode: manual, channel: bypass)
fbypass_ctl bp_module all 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 enable_bypass
- Set active channels at the first site to bypass mode (mode: manual, channel: bypass)
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 enable_bypass
- Set active channels at the second site to bypass mode (mode: manual, channel: bypass)
fbypass_ctl bp_module 1 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 enable_bypass
- Remove active channels on all sites from bypass to "combat mode" (mode: auto, channel: primary)
fbypass_ctl bp_module all 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 disable_bypass
- Remove active channels on the first site from bypass to "combat mode" (mode: auto, channel: primary)
fbypass_ctl bp_module 0 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 disable_bypass
- Remove active channels on the second site from bypass to "combat mode" (mode: auto, channel: primary)
fbypass_ctl bp_module 1 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 disable_bypass
PC Bypass Management Guide
- Go to Start → Control Panel → Programs and Features → Turn Windows features on or off. Check "Windows Subsystem for Linux"
- Download Debian from the Microsoft Store.
- In Debian, install the following software:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install telnet sudo apt-get install openssh-client
- In Debian, create a folder
mkdir -p /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/
- Copy the folder from the NPB
scp -r user@10.19.1.222:/var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/. /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/
When entering management commands, specify the full path to the script, for example:
/var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/app_bash/cmd_bypass_ctl.sh
FastBypass monitor
If there is a software failure on DPI, the NPB removes the DPI from the stack and redistributes the load among the remaining DPIs.
If more than two DPI nodes fail, the entire system switches to bypass mode.
If the link on a DPI fails, NPB redistributes the load among the remaining DPIs.
fastbypass_monitor (referred to as "daemon" further in the documentation and script) is a tool for monitoring and managing the state of network interfaces connected to Bypass network cards.
The daemon reacts to HEARTBEAT signals received from DPI on specific ports defined in the configuration file. If HEARTBEAT signals are not received according to the configuration rules, the daemon performs specific actions such as deleting or creating IP addresses connected to the Bypass cards and enabling or disabling certain network interfaces.
Hardware Requirements
OS: OpenSwitch 2+ / Debian 9+
Python: 2.7.9
Key Features
- Monitoring HEARTBEAT signals from DPI on specified ports.
- Dynamic management of IP addresses and network interfaces.
Installation
- Copy the installation package
fastbypass_monitor-X.X.XX.debto the host machine. - Run the following command from the directory where the package is located:
sudo dpkg -i fastbypass_monitor-X.X.XX.deb
After installation, the daemon becomes manageable through the system manager (systemctl).
The configuration file is available at /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/.env
A sample configuration file can be found at /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/sample.env
Daemon logs are stored at /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/logs/
Usage
After installation, the daemon runs automatically. Upon reboot, it starts after the network service has successfully launched.
Manage the daemon using system manager commands.

sudo su - and enter the password to enable this mode.
Start the daemon:
sudo systemctl start fastbypass_monitor
Alias:
fbypass_ctl start
Restart the daemon:
sudo systemctl restart fastbypass_monitor
Alias:
fbypass_ctl restart
Reload the daemon without stopping:
sudo systemctl reload fastbypass_monitor
Alias:
fbypass_ctl reload
Stop the daemon:
sudo systemctl stop fastbypass_monitor
Alias:
fbypass_ctl stop
Check the daemon’s status:
sudo systemctl status fastbypass_monitor
Alias:
fbypass_ctl status
View the last few lines of the log file in real-time:
tail -f /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/logs/fastbypass_monitor.log
Alias:
fbypass_ctl tailf
Output the last 100 lines of the log:
tail -n 100 /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/logs/fastbypass_monitor.log
Alias:
fbypass_ctl tail 100
Stop the daemon and remove IPs from Bypass cards, forcing the system into bypass mode:
fbypass_ctl force_on
Stop the daemon and add IPs to Bypass cards, forcing the system into normal mode:
fbypass_ctl force_off
Add the daemon to startup:
fbypass_ctl enable
Remove the daemon from startup:
fbypass_ctl disable
To configure and launch the daemon with new settings, edit the configuration file and restart or stop and start the daemon.
The daemon configuration is located at /var/fastbypass_monitor/backend/.env
In case of a critical error, the daemon will restart automatically.
Using sudo systemctl reload fastbypass_monitor will reload the configuration without stopping the daemon, shutting down removed components, and adding new ones.
During startup and reload, the daemon does not manage interfaces and IPs until all listeners report their statuses. After a restart, the daemon remains in its previous state until receiving updates from all listeners.
Local and Global States: Bypass Mode
The daemon manages interfaces based on either a global state (depending on all listeners) or a local state (specific to individual listeners).
For instance, if you list interfaces in the global settings, they will be enabled or disabled based on the daemon’s overall state. If the daemon fails to receive enough signals, the interfaces are disabled.
Example:
LISTEN_CUBRO_IFS=<interface list> LISTEN_SHUTDOWN_CUBRO_IFS_WHEN_BYPASS=1
Each listener can also have its own interface list that it manages based on its state.
Example:
LISTEN_CUBRO_IFS[0]=<interface list> LISTEN_SHUTDOWN_CUBRO_IFS_WHEN_BYPASS[0]=1
If an interface appears in multiple listeners' lists, it switches to bypass mode if any listener stops receiving signals. The interface returns to normal mode only if all listeners are active.
If an interface appears in both local and global settings, it remains in bypass mode until the corresponding listener starts receiving signals and the daemon switches to normal mode.
Configuration
Minimal Configuration
A minimal configuration requires specifying at least one interface, IP address, and port for receiving HEARTBEAT signals, along with one interface and IP for Bypass cards.
Example:
LOG_LEVEL=INFO LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_IFS=eth0 BYPASS_CARD_IFS=eth0 LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_FAILED=1 LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_ATTEMPTS=1 LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT=3000 LISTEN_HB_HOST[0]=192.168.1.202 LISTEN_HB_PORT[0]=3000 LISTEN_HB_HOST[1]=192.168.1.202 LISTEN_HB_PORT[1]=3100 BYPASS_CARD_HOST[0]=192.168.1.211 BYPASS_CARD_HOST[1]=192.168.1.212
This example configures the daemon to receive HEARTBEAT signals on interface eth0 at IP 192.168.1.202 and ports 3000 and 3100.
Bypass cards are connected via eth0 at IPs 192.168.1.211 and 192.168.1.212.
Default listener values:
LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_ATTEMPTS: 1
LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT: 3000 ms
If a listener fails to receive a signal after one attempt within 3000 ms, it is marked as failed.
If the number of failed listeners meets or exceeds the threshold (LISTEN_HEARTBEAT_FAILED), the daemon switches to bypass mode and removes IPs from Bypass cards.
When signals are restored, the listener resumes normal operation.
If the number of failed listeners falls below the threshold, the daemon switches back to NORMAL mode and restores the IPs for the Bypass cards.